Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>

































 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
mAb Matrix
As a leading manufacturer of recombinant proteins and other critical reagents to support the development of target therapeutics, vaccines, and diagnostics, ACROBiosystems has established an antibody product line named "mAb matrix". There are diverse antibodies in mAb matrix including biological target antibodies, biomarker antibodies, receptor antibodies, cytokine antibodies (interleukin antibodies, chemokine antibodies), virus antibodies, small molecular inhibitors antibodies, diagnostic antibodies, process engineering antibodies, etc.
The "antibody matrix" series products are characterized with high-specificity and high-sensitivity, and they are suitable for the methodology construction of both diagnosis and the entire process in the biopharmaceutical R&D, helping to accelerate the medicine R&D and commercial process.
TNF-α is the most widely studied pleiotropic cytokine of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily. As an important cytokine in the innate immune response, TNF-α plays a key role in the direct host defense against invading microorganisms before the activation of the adaptive immune system. It is primarily produced by the activation of membrane-bounded pattern recognition molecules such as toll-like receptors by macrophages, which detect common bacterial cell surface products. TNF-α is also produced by several other pro-inflammatory cells, including monocytes, dendritic cells, B cells, CD4+ cells, neutrophils, mast cells, and eosinophils, as well as structural cells (i.e., fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and smooth muscle cells).
TNF-α is initially a biologically active, 26KD membrane-anchored precursor protein (mTNF-α) that is subsequently cleaved by TNF-α converting enzyme (TACE) to form a 17KD free protein. These proteins form biologically active homotrimers that act on the ubiquitously expressed TNF-α receptors 1 and 2. This receptor-ligand interaction results in intracellular signaling without internalizing the complex, and the phosphorylation of IkBa, which activates the nuclear factor-kB (p50-p65) heterodimer, which further interacts with DNA chromatin structure to increase the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes such as IL-1B, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α. The activating response of TNF-α is balanced by the shedding of the extracellular domain of the TNF-α receptor.
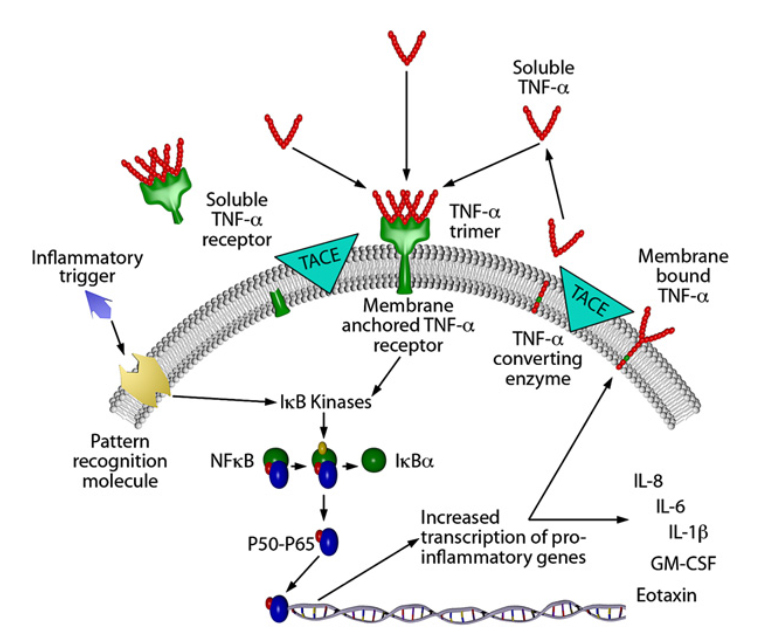
The biological mechanism and signal transduction of TNF-α
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Species | Product Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-alpha | TNA-H4211 | Human | ActiveMax® Human TNF-alpha Protein, Tag Free, low endotoxin (active trimer) (MALS verified) |
| TNA-H5228 | Human | Human TNF-alpha Protein, His Tag (active trimer) (MALS verified) | |
| TNA-H82E3 | Human | Biotinylated Human TNF-alpha Protein, His,Avitag™ (active trimer) (MALS verified) | |
| TNA-H8211 | Human | Biotinylated Human TNF-alpha Protein, epitope tag free, ultra sensitivity (primary amine labeling) (active trimer) (MALS verified) | |
| TNA-M82E9 | Mouse | Biotinylated Mouse TNF-alpha Protein, His,Avitag™ (active trimer) (MALS verified) | |
| TNA-C52H3 | Canine | Canine TNF-alpha Protein, His Tag, active trimer (MALS verified) | |
| TNFR1 | TN1-H5222 | Human | Human TNFR1 / CD120a / TNFRSF1A Protein, His Tag |
| TN1-H5251 | Human | Human TNFR1 / CD120a / TNFRSF1A Protein, Fc Tag (MALS verified) | |
| TNFR2 | TN2-H5227 | Human | Human TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein, His Tag |
| TN2-H82E3 | Human | Biotinylated Human TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein, His,Avitag™ | |
| TN2-M52H8 | Mouse | Mouse TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein, His Tag | |
| TN2-C52H7 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein, His Tag |
TNF-α is a major pleiotropic mediator of acute and chronic systemic inflammatory responses, regulating both apoptosis and proliferation, and promoting the production of other chemokines and cytokines. It is also involved in a range of physiological processes, such as antitumor responses, control of inflammation, and immune system homeostasis. TNF-α is also one of the most important pro-inflammatory cytokines in the innate immune response. The TNF-α signaling pathway plays a crucial role in cytokine release storm (CRS), and dysregulation of TNF-α signaling can trigger CRS. Elevation of TNF-α may accelerate viral infection, organ damage, and block cytokine-mediated inflammatory cell death signaling pathways which may benefit COVID-19 patients or other infectious diseases and limit tissue damage.
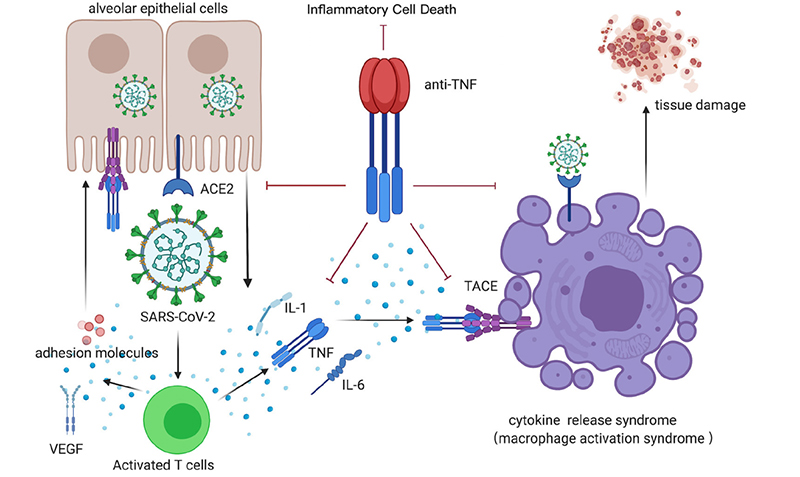
Anti-TNF-α therapy for CRS following COVID-19 infection
Some studies have pointed out that the adoption of anti-TNF therapy may be limited by its potential side effects. It is particularly important to distinguish patients with poor prognosis and improve clinical outcomes from patients who can recover on their own and find the treatment time for COVID-19 patients, so as to minimize potential risks associated with immunosuppression.
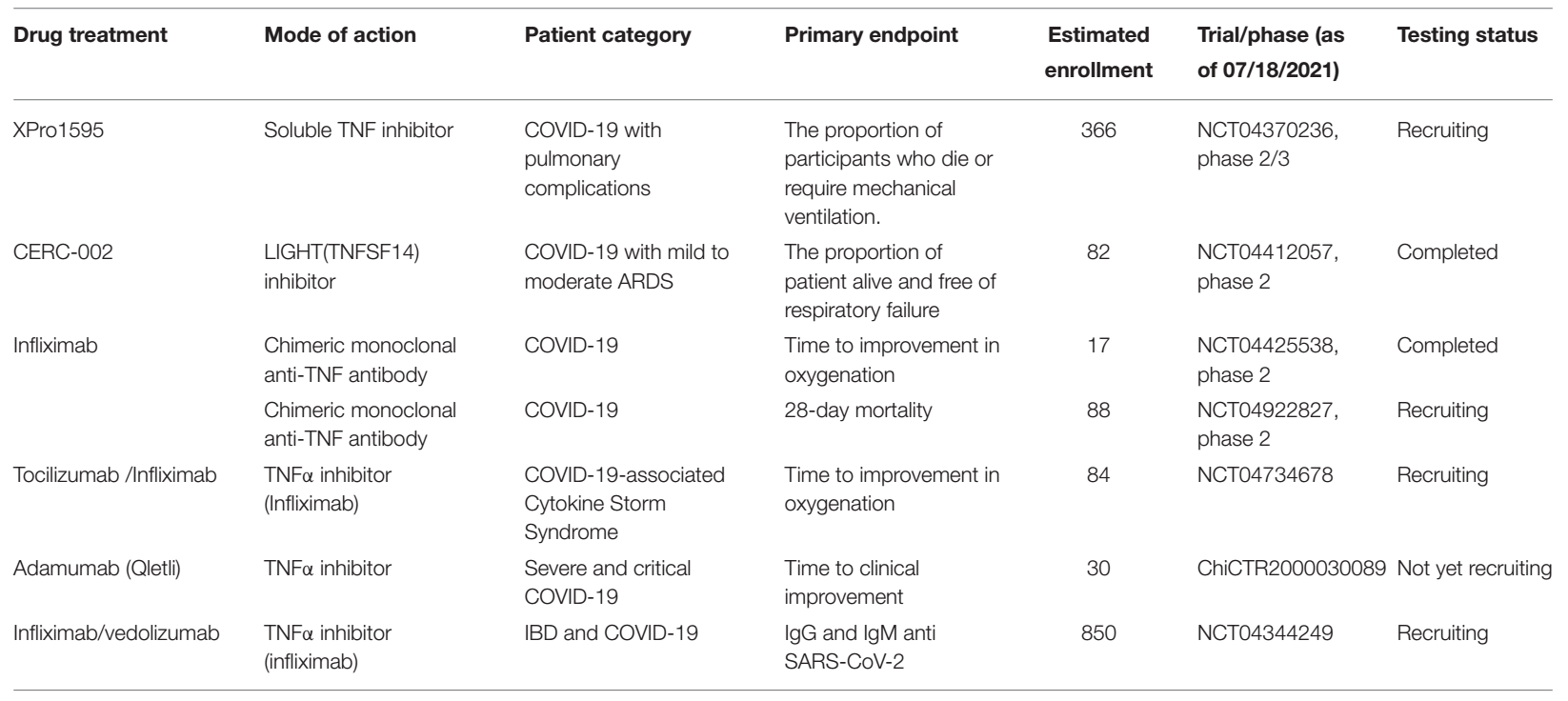
Drugs targeting TNF or its receptors in clinical studies of COVID-19 patients
As we mentioned before, TNF-α is a powerful pro-inflammatory cytokine with pleiotropic effects on multiple cell types and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A variety of anti-TNF drugs have been successfully used to treat chronic inflammatory diseases such as Crohn's disease, RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and psoriasis. The clinical efficacy of different anti-TNF drugs may be due to their different effects on transmembrane TNF-α cells.
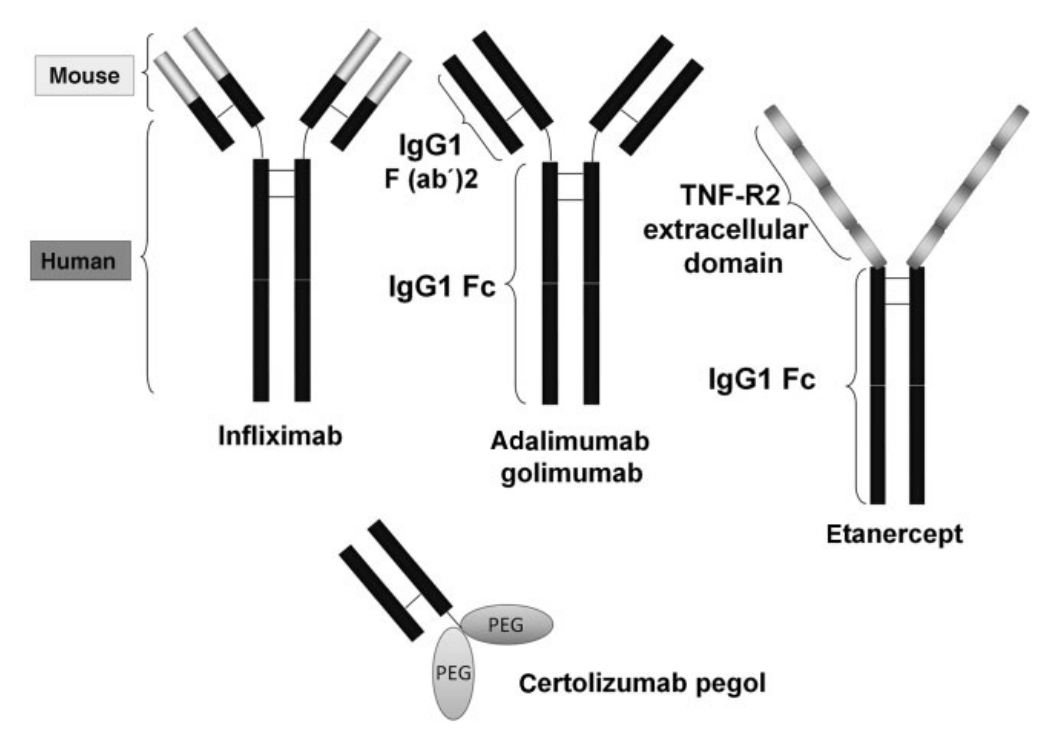
Different anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibodies
- In terms of structure, Infliximab, Adalimumab, and Golimumab are monoclonal antibodies against human TNF-α. Infliximab is a human-mouse chimeric anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody, consisting of a murine variable region and a human variable region IgG1 constant region. Adalimumab and Golimumab are fully humanized anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibodies. Etanercept is composed of two extracellular parts Human TNF-R2 (p75 TNF receptor) linked to the Fc part (CH2 and CH3 domains) of human IgG1. Certolizumab is an anti-TNFα- Fab fragment of IgG1 mAb, the hinge region is covalently linked to two 20KDa polyethylene glycol cross-linked chains, lacking the Fc fragment
- Their binding properties are different, Infliximab can bind both monomeric and trimeric forms of soluble TNF-α, while Etanercept can only bind the trimer. Infliximab forms stable complexes with soluble TNF-α, whereas Etanercept forms relatively unstable complexes. Each Infliximab molecule can bind to two TNF-α molecules, and three Infliximab molecules can bind to the TNF-α homotrimer. In contrast, Etanercept is thought to form a 1:1 complex with TNF-α trimers。
ACROBiosystems has launched two TNF-α antibodies derived from different clones:
![]() The immunogen is Human TNF-alpha Protein, His Tag (active trimer) (MALS verified) (Cat. No. TNA-H5228)
The immunogen is Human TNF-alpha Protein, His Tag (active trimer) (MALS verified) (Cat. No. TNA-H5228)
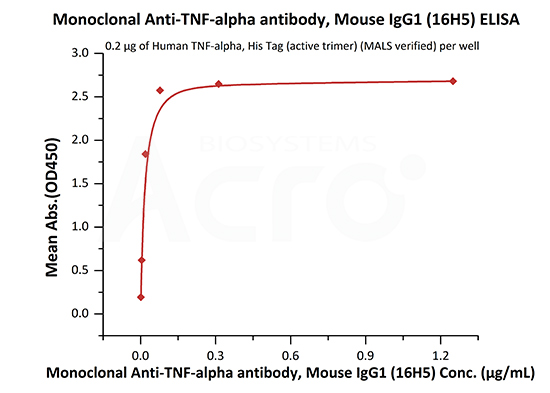
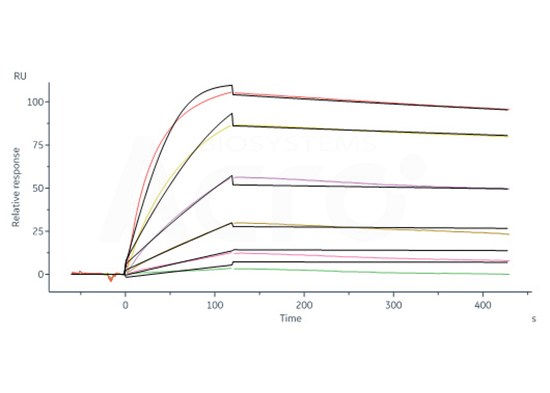
![]() Validated by ELISA and BLI, TNF-α antibody can specifically bind to Human TNF-α homotrimeric protein
Validated by ELISA and BLI, TNF-α antibody can specifically bind to Human TNF-α homotrimeric protein
![]() Suitable for the detection of TNF-α by antibodies sandwich method.
Suitable for the detection of TNF-α by antibodies sandwich method.
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Species | Product Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-TNFα Antibody | TNA-Y58 | Mouse | Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) |
| TNA-Y59 | Mouse | Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (16H5) |
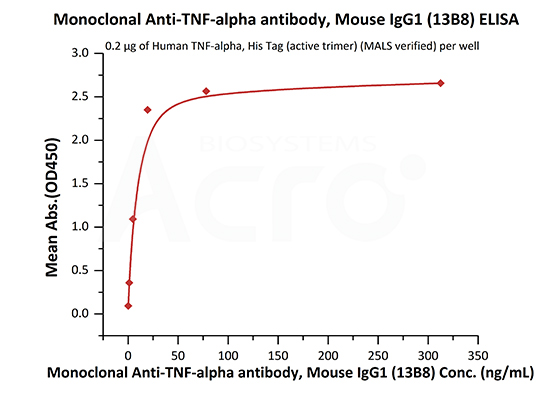
Immobilized Human TNF-alpha, His Tag (active trimer) (Cat. No. TNA-H5228) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) (Cat. No. TNA-Y58) with a linear range of 0.3-20 ng/mL (QC tested).
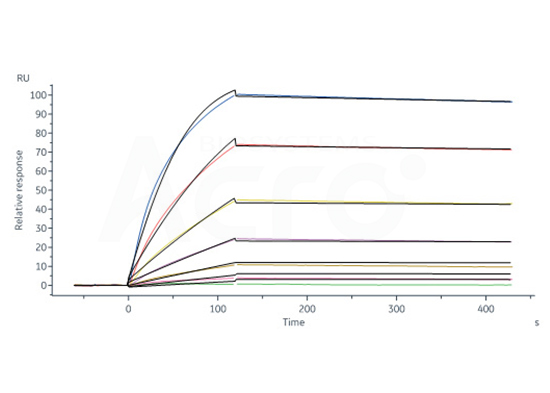
Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) (Cat. No. TNA-Y58) captured on CM5 chip via anti-mouse antibodies surface can bind Human TNF-alpha, His Tag (active trimer) (Cat. No. TNA-H5228) with an affinity constant of 0.323 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K).
>>[Newly Launched] Three anti-IFN γ antibodies in ACRO’s “mAb Matrix”
1. Christopher Brightling, Mike Berry, Yassine Amrani. Targeting TNF-α: A novel therapeutic approach for asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2007.10.028.
2. Guo Y, Hu K, Li Y, Lu C, Ling K, Cai C, Wang W, Ye D. Targeting TNF-α for COVID-19: Recent Advanced and Controversies (2022). Front. Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.833967
3. Takahiko Horiuchi, Hiroki Mitoma, Shin-ichi Harashima, Hiroshi Tsukamoto, Terufumi Shimoda. Transmembrane TNF-α: structure, function and interaction with anti-TNF agents. Rheumatology (2010). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keq031
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.