
Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>


































 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Pharmacokinetics (PK) is a branch of science dedicated to the quantitative analysis of absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of drug molecules within the body of a living organism. All pre-clinical and clinical studies include the measurement of serum drug concentration, both in animals and in patients, at different points after drug administration. The result is an important indicator of the drug’s pharmacokinetic properties and is pertinently relevant to dosing recommendations.
The booming market of biologic drugs, driven by a flurry of success with monoclonal antibodies, brings the need for standard high throughput assays to evaluate the content of mAbs in serum samples. There are several types of assay designs based on different principles. The table below listed three most common ELISA setups for serum antibody detection, and their general advantages and disadvantages. To evaluate their performance in real applications, we tested them in the following case studies measuring the concentration of anti-PD1 mAb in serum samples.
| Method | Coating | Sample | Secondary Antibody | Advantage | Disadvantage | Case Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indirect assay | Antigen | Serum | Goat anti-human IgG | Simple | High background | Case I |
| Antibody-directed competitive assay | Antigen | Serum with labeled competition antibody | SA-HRP | Low background | Additional reagent/labeling required | Case II |
| Ligand-directed competitive assay | Natural ligand for the antigen | Serum with labeled PD-1 | SA-HRP | Low background | Narrow detection range | Case III |
Please feel free to contact us by pk@acrobiosystems.com if you have any questions.
Equipment:BMG CLARIOstar microplate reader
Sample:Serum samples containing a monoclonal PD-1 antibody
Main Reagents:
Protocol:
Protocol:
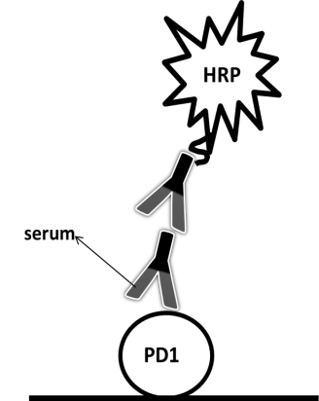
Equipment:BMG CLARIOstar microplate reader
Sample:Serum samples containing a monoclonal PD-1 antibody
Main Reagents:
Protocol:
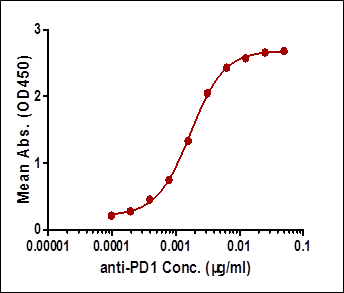
Result:
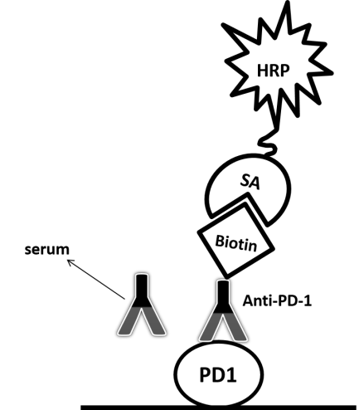
Related Products:
Equipment:BMG CLARIOstar microplate reader
Sample:Serum samples containing a monoclonal PD-1 antibody
Main Reagents:
Simplified Protocol:
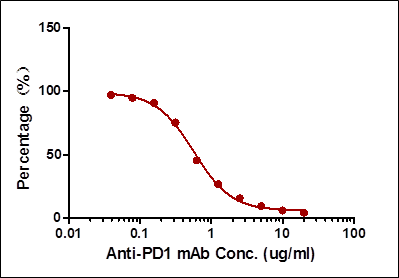
Result:

| Case | Detection Range (µg/mL) | Sensitivity (µg/mL) | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case I:Indirect ELISA | 0.19-6.25 | 0.19 | High background |
| Case II:Antibody-directed competitive ELISA | 0.78-25 | 0.78 | Very low background |
| Case III:Ligand-directed competitive ELISA | 1.565-6.25 | 1.565 | Very low background |
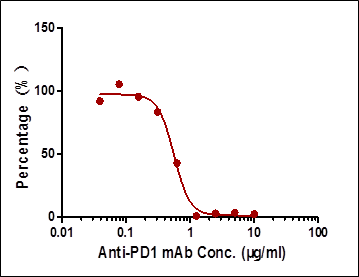
Among the aforementioned three assay designs, the ligand-directed competitive ELISA (Case III) has the narrowest detection range and lowest sensitivity, indicating that it’s not the best solution for the application. The sensitivity for the indirect ELISA is the best. However, the use of goat anti-human IgG as secondary antibody results in high background due to unspecific binding, and therefore require pre-dilution before analyses (Fig. 4A). On the other hand, the antibody-directed competitive ELISA uses HRP-conjugated Streptavidin for secondary detection, which minimize the background interference (Fig. 4B). In addition, it also has the widest detection range among the group, although the sensitivity is lower than the indirect method.
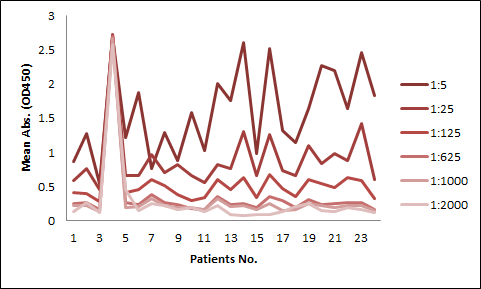
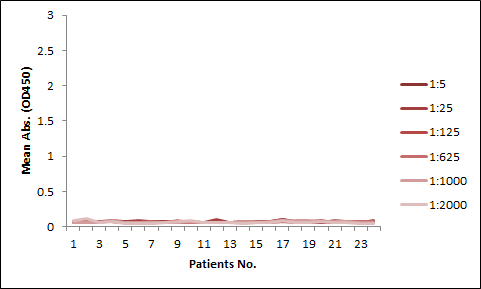
In most applications, the background issue is a bigger concern than detection sensitivity, as a detection sensitivity of less than 1 µg/ml is already good enough. Therefore, we opt to use the antibody-directed competitive ELISA for the PK kits.
We have launched kits for the studies of CTLA-4, PD-1, and HER-2, respectively, in both humans, and common experimental animals.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.







