Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>


































 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
> Solutions for RABV vaccine and drug development

Rabies virus (RABV) is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in humans and animals, occurring in more than 150 countries and territories. Once clinical symptoms appear, rabies is virtually 100% fatal. Despite the availability of post-exposure vaccines, rabies remains a global health threat.
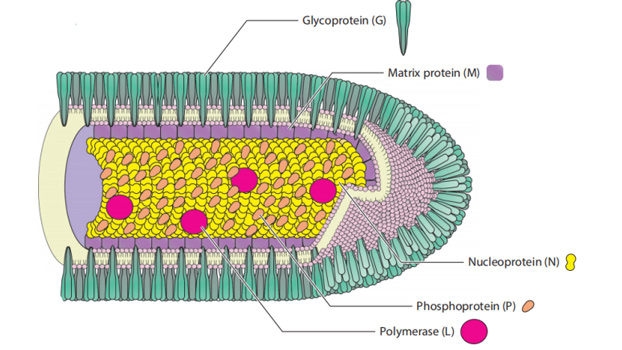
The causative agent of rabies, RABV, is a negative-stranded RNA virus of the genus Lyssavirus. RABV is a member of the Rhabdoviridae family, named for the characteristic rod- or bullet-shaped rhabdovirus virion observed by electron microscopy. Rhabdovirus virions, like other negative-stranded RNA viruses, are composed of a highly stable and organized complex of genomic RNA and nucleoprotein, contained in a lipid envelope derived from the host cell membrane.
Existing vaccines target the rabies virus glycoprotein (RABV-G). However, these vaccines induce short-lived immune responses potentially due to the heterogeneous nature of RABV-G under physiological conditions. Recent research suggests that incorporating trimeric, prefusion RABV-G bound to a potent and broadly neutralizing antibody into vaccine design is crucial for presenting the correct conformation of the protein and eliciting a robust immune response. Nucleic acid-based vaccines offer an alternative approach, potentially bypass purification issues, but must still ensure the expression of glycoproteins with the correct conformation and quaternary assembly.
While RABV-G remains a primary focus for vaccine development, the nucleoprotein (N) has emerged as a promising alternative target. Studies demonstrate that N can induce robust T helper cell responses and long-lasting humoral immunity, making it a valuable candidate for next-generation rabies vaccines.
N plays a central role in RABV replication, encapsidating the viral genome and forming the viral ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex, which serves as the template for viral transcription and replication. Additionally, the amino acids at positions 273 and 394 in the N protein are important for both evasion of the host RIG-I-mediated antiviral response and pathogenicity.
The development and improvement of vaccines remain the current prevention and control of the principal means of RABV infection. Explore our comprehensive suite of solutions for RABV vaccine development!
![]() Mouse Anti-RABV Nucleoprotein Antibody IgG Titer Serologic Assay Kit (ELISA) are available!NEW
Mouse Anti-RABV Nucleoprotein Antibody IgG Titer Serologic Assay Kit (ELISA) are available!NEW
![]() Native, structurally verified trimeric glycoprotein (G) & RABV-G specific antibodies.
Native, structurally verified trimeric glycoprotein (G) & RABV-G specific antibodies.
![]() RABV Nucleoprotein (N) verified through ELISA with specific antibodies.
RABV Nucleoprotein (N) verified through ELISA with specific antibodies.
![]() High quality RABV-G Antigen/antibody ELISA kits
High quality RABV-G Antigen/antibody ELISA kits
| Product Type | Molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description |
|---|
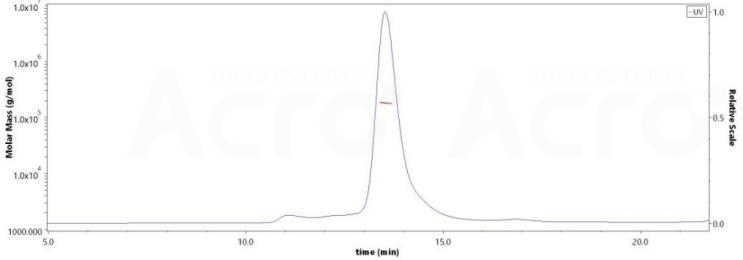
Purity of RABV Glycoprotein G, His Tag (Cat. No. RAG-V55H5) exceeds 85%, with a verified molecular weight of approximately 165-195 kDa by SEC-MALS analysis.
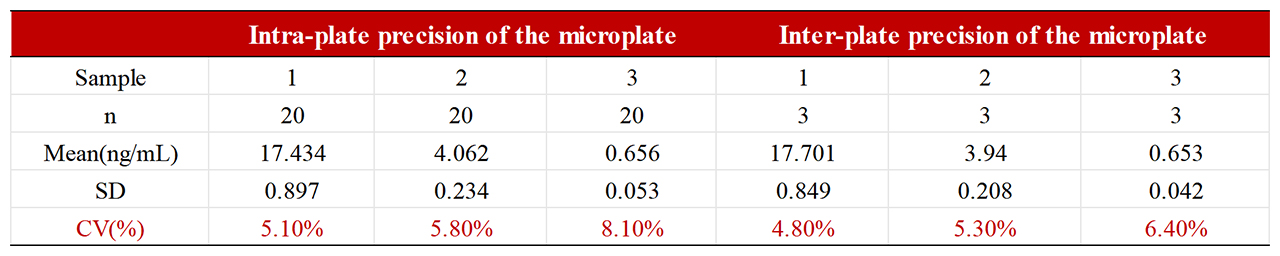
To assess the precision of RAS-A167, repeat it 20 times to assess the accuracy within the plates and 3 times for three known concentrations to assess the accuracy between the plates. The within and inter-plate precision of the project is CV<9%, better than the standard range stated by the kit (CV<15%).
To assess the dilution linearity of RAS-A167, high-value spiked samples were analyzed after gradient dilution. The results showed that the average recovery of all analyzed samples was between 80% and 120%, better than the accepted range.
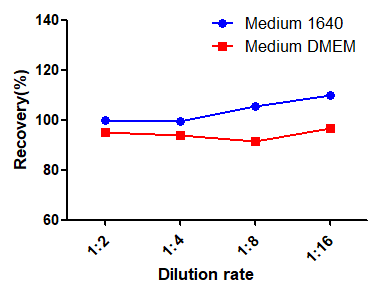
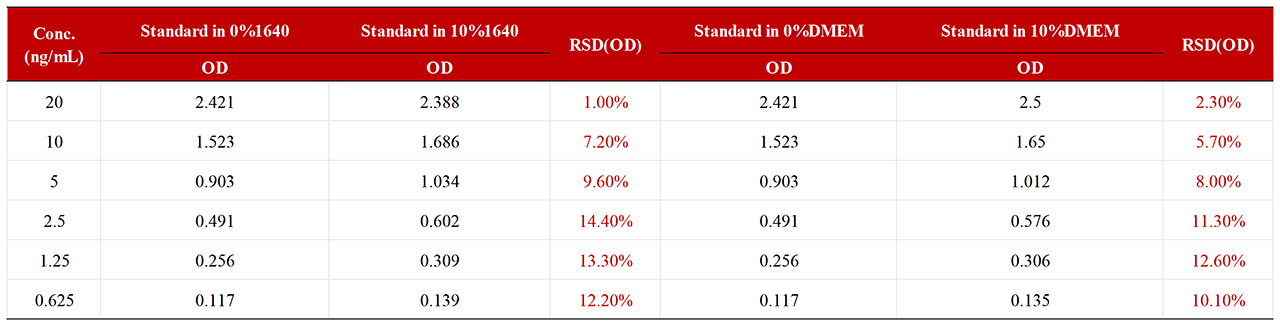
To assess the matrix effect of RAS-A167, different proportions of media interfered with the standard, which showed that 10% of 1640 media and 10% of DMEM media met the standard (RSD<15%). If 100% medium is used, MRD=10 is recommended.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.