Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>


































 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
> Protéines transmembranaires multi-passes et plate-formes technologiques
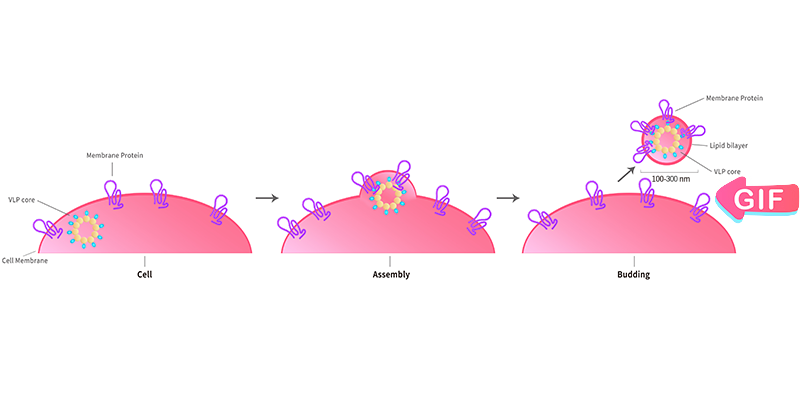
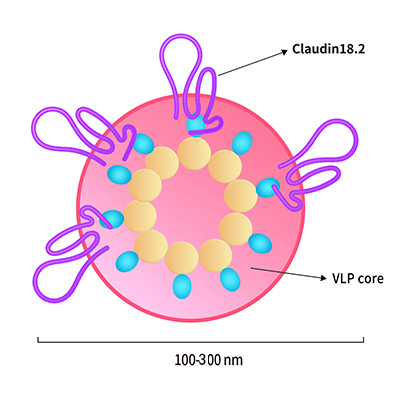
La plate-forme technologique VLP (Virus like particules, particules pseudo-virales) basée sur le système d'expression HEK293 est spécialement mise en place par ACROBiosystems pour exprimer les PT à la surface de la cellule hôte. La protéine d'enveloppe/capside virale transforme ensuite ces surfaces cellulaires en particules de bicouche lipidique soluble avec des protéines hautement concentrées utilisables pour la vaccination et le crible par les anticorps. Le complexe protéine membranaire-VLP affiche des PT multi-passes correctement repliées dans sa membrane cellulaire induisant et criblant des anticorps fonctionnels qui reconnaissent la conformation naturelle de la cible. En plus de fournir des PT multi-passes basées sur les VLP dans notre catalogue, ACRO fournit également des services personnalisés.
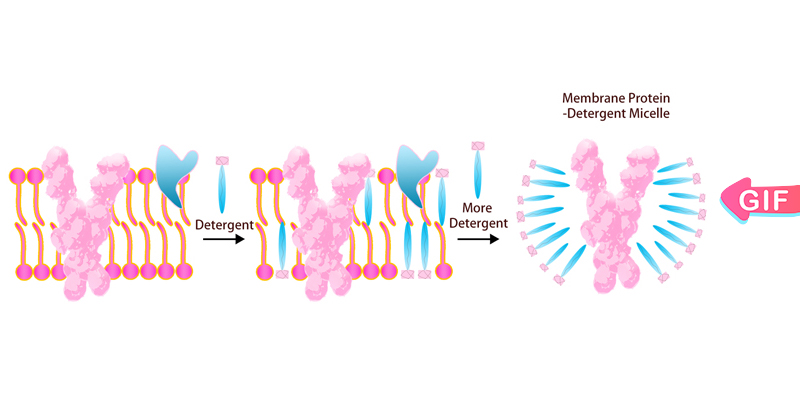
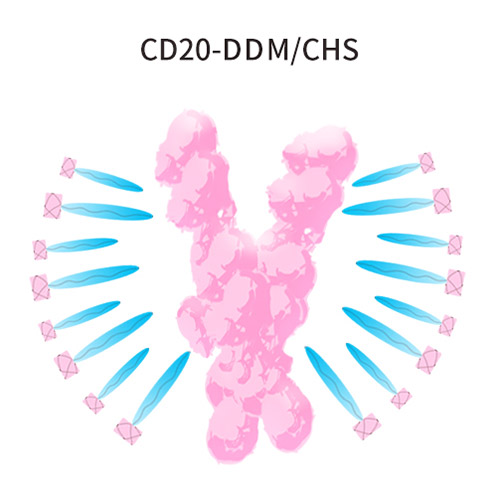
La région transmembranaire des PT multi-passes est hautement hydrophobe et il est difficile de maintenir la conformation correcte dans les tampons ordinaires une fois extraits de la membrane cellulaire. Ce problème peut être résolu par l'ajout de détergents. ACROBiosystems a mis en place une plate-forme complète pour l'expression, la purification et la stabilisation de cellules d'insectes et de cellules de mammifères pour les PT cibles de médicaments difficiles. ACRO effectue un criblage au détergent, y compris DDM/CHS (Cat. N° DC-11) pour augmenter la solubilité et assurer le repliement natif de cette protéine in vitro.
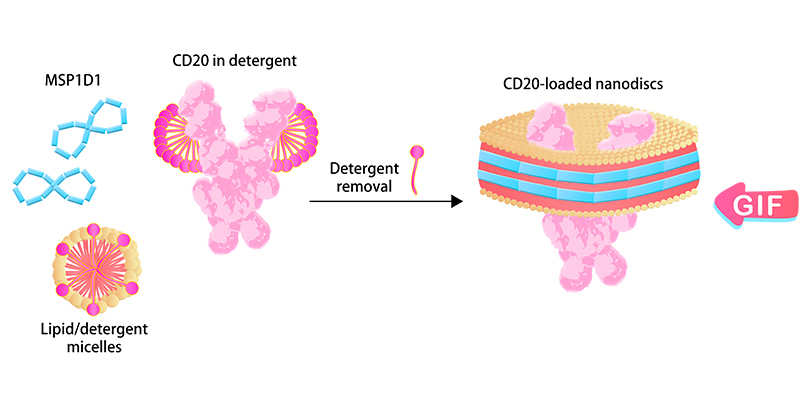
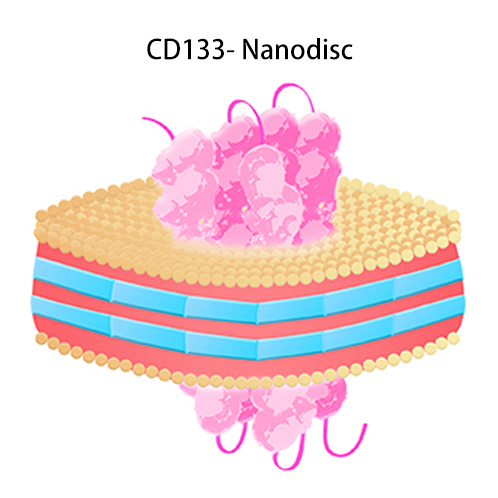
"Nanodisc" est une structure membranaire bicouche phospholipidique synthétique composée de protéines d'échafaudage membranaire (MSP) et de molécules phospholipidiques. Les PT peuvent être intégrées dans la structure spéciale du Nanodisc après élimination du détergent afin de maintenir son repliement natif, conserver son activité biologique et présenter une hydrophilie améliorée pour une large gamme d'applications. Par exemple, la formulation sans détergent des PT à base de Nanodisc est compatible avec les tests d'expression CAR. ACROBiosystems a effectué une optimisation et une amélioration continues du processus d'assemblage pour le rendre adapté à la production industrielle à grande échelle. Les efforts d'ACRO ont assuré un approvisionnement stable à long terme de produits PT basés sur Nanodisc pour l'industrie biopharmaceutique.
VLP
Micelle de détergent
Nanodisc
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Preorder/Order |
|---|
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Preorder/Order |
|---|
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Preorder/Order |
|---|
Les protocoles SPR suivants sont disponibles gratuitement.
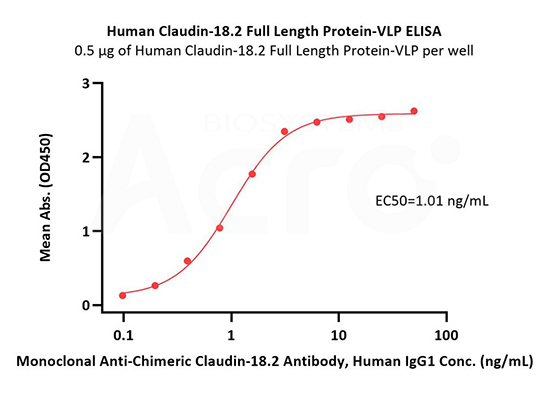
Immobilized Human Claudin-18.2 Full Length Protein-VLP (Cat. No. CL2-H52P7) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Monoclonal Anti-Chimeric Claudin-18.2 Antibody, Human IgG1 with a linear range of 0.2-3 ng/mL (QC tested).
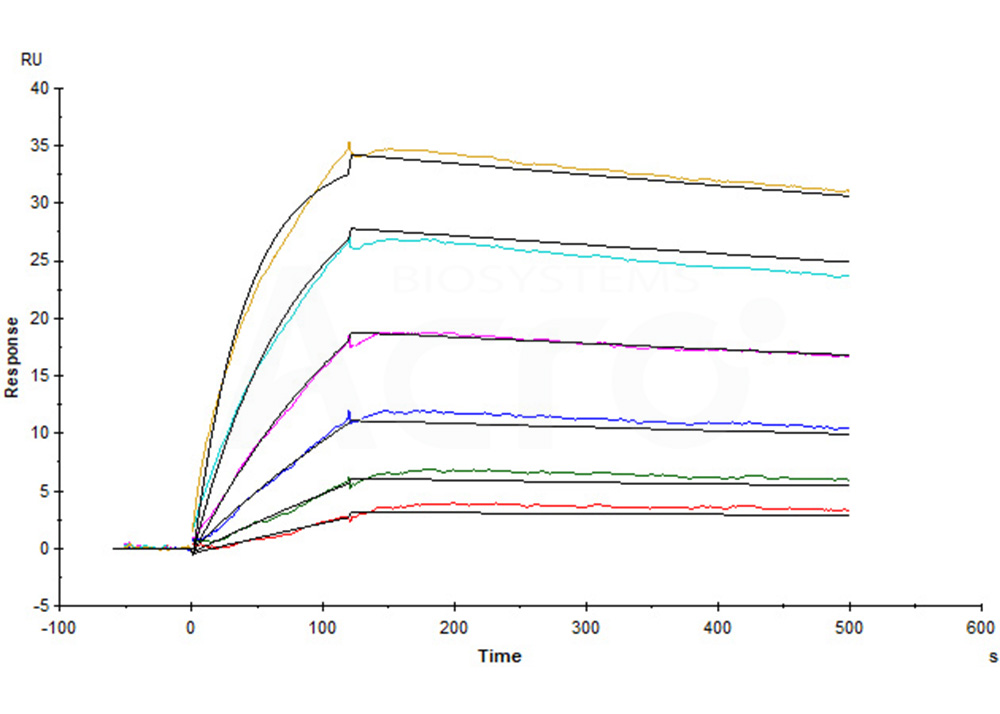
Human Claudin-18.2 Full Length Protein-VLP (Cat. No. CL2-H52P7) captured on CM5 Chip via Anti-Claudin-18.2 antibody can bind Anti-Claudin-18.2 antibody with an affinity constant of 0.374 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore T200) (Routinely tested).
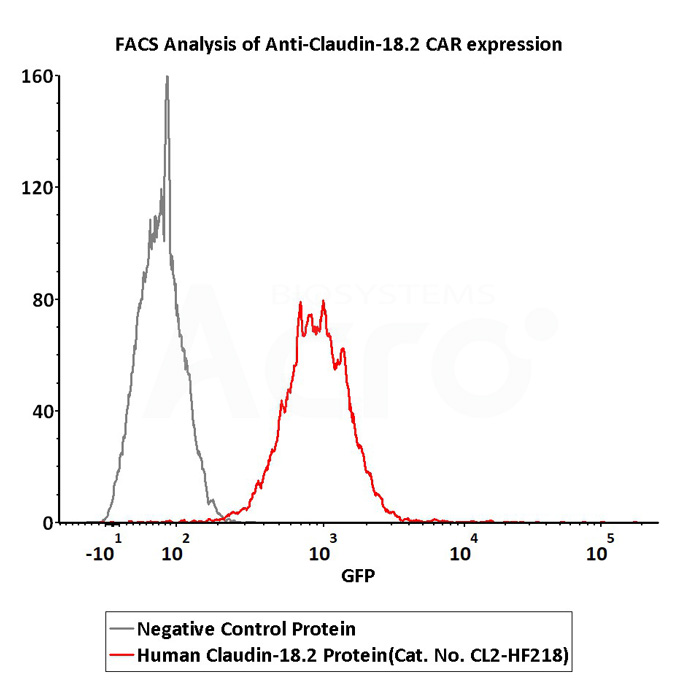
2e5 of Anti-Claudin-18.2 CAR-293 cells were stained with 100 μL of 3 μg/mL of Fluorescent Human Claudin-18.2 Full Length Protein-VLP (Cat. No.CL2-HF218) and negative control protein respectively, FITC signals was used to evaluate the binding activity (QC tested).
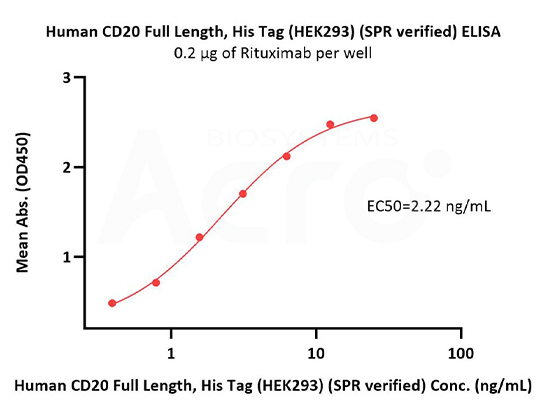
Immobilized Rituximab at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human CD20 Full Length Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. CD0-H52H3) with a linear range of 0.4-3 ng/mL (in presence of DDM and CHS) (QC tested).
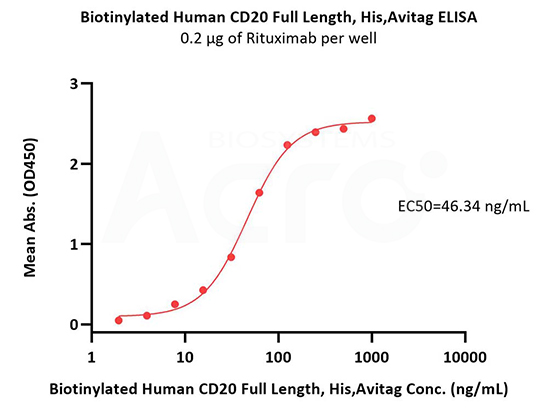
Immobilized Rituximab at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Biotinylated Human CD20 Full Length, His,Avitag (Cat. No. CD0-H82E5) with a linear range of 4-63 ng/mL (in presence of DDM and CHS) (QC tested).
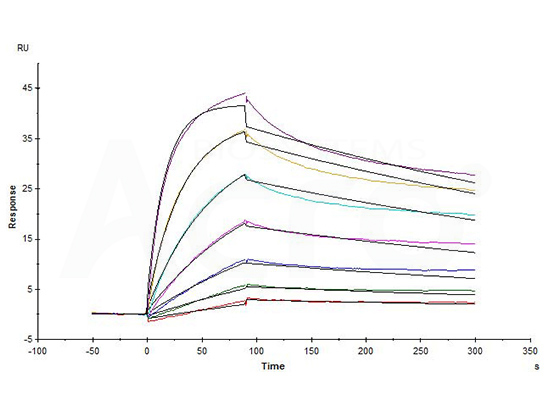
Biotinylated Human CD20 Full Length, His,Avitag (Cat. No. CD0-H82E5) captured on Biotin CAP-Series S Sensor Chip can bind Rituximab with an affinity constant of 1.73 nM as determined in a SPR assay (in presence of DDM and CHS) (Biacore T200) (QC tested).
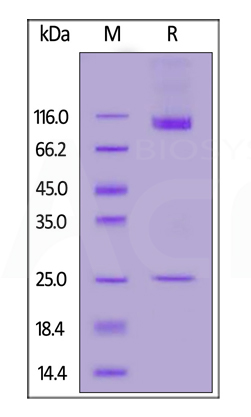
Human CD133 Full Length, His Tag (Nanodisc) (Cat. No. CD3-H52H1) on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained overnight with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 90%.
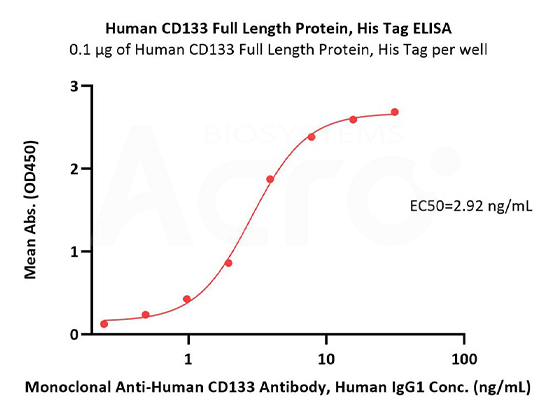
Immobilized Human CD133 Full Length Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. CD3-H52H1) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Monoclonal Anti-Human CD133 Antibody, Human IgG1 with a linear range of 0.2-4 ng/mL (QC tested).

Our Claudin18.2 has been developed with VLP and DMM/CHS platforms. Both of these versions are suitable for immunization and screening. However, the VLP version may be preferred for improved immunogenicity. For accurate affinity measurements, we recommend using the DDM/CHS version (the detergent version).
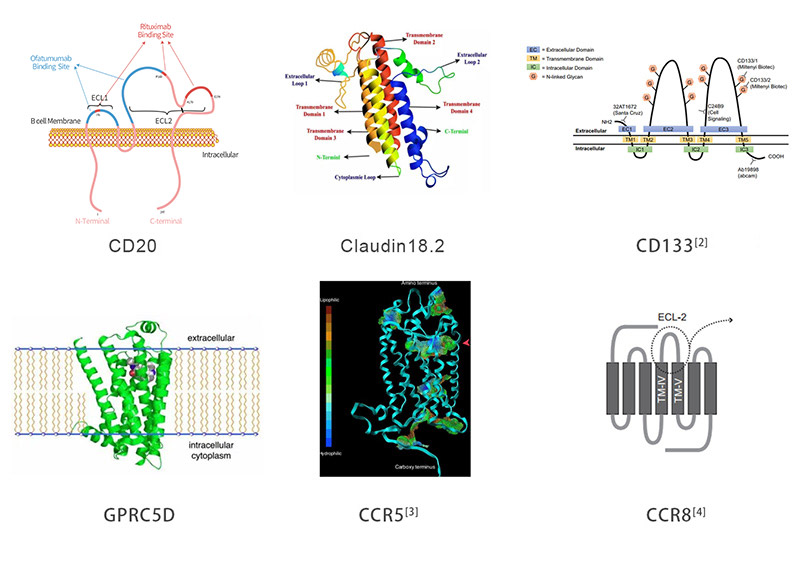
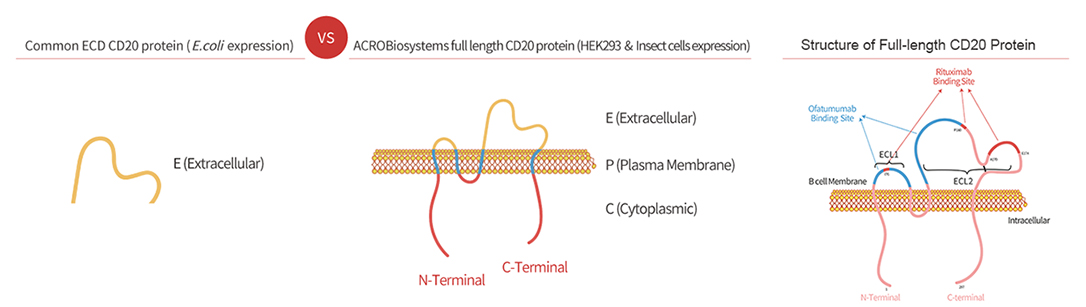
Multi-pass transmembrane proteins span the cell membrane multiple times forming multiple extracellular domains. For example, Claudin18.2, CD20, and CD133 have two extracellular loops (ECLs) with each ECL having specific functions and interactions with each other. Full length can ensure that the protein conformation is biologically relevant while enabling the ECL to be completely exposed for improved screening of ideal antibodies. As the figure below illustrates, the full length is active and relevant compared to isolated extracellular domain. It is not the case that ACRO always emphasizes full length proteins, but drug discovery R&D work needs the full-length multi-pass transmembrane proteins. Indeed, when compared, the activity of only the ECL region is worse than that of the full-length protein. ACRO is committed to providing the high quality and relevant products that meet customers' needs.
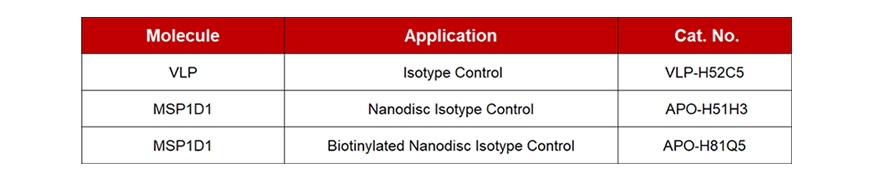
The influence of non-specific antibodies cannot be ignored. Using membrane proteins under the VLP and Nanodisc platforms may produce non-specific antibodies. Both of our platforms have corresponding isotype controls for reverse-screening and excluding non-specific antibodies. Membrane protein-VLP has an isotype control product (Cat. No. VLP-NF2P4). Membrane protein-Nanodisc has two isotype control products, one of which is MSP1D1(Cat. No. APO-H51H3) as the isotype control for tag free version. If a biotinylated membrane protein-Nanodisc is used, MSP1D1(Cat. No. APO-H81Q5) can be used as the isotype control.
Nanodisc-membrane proteins are quite different from detergent stabilized membrane proteins. First of all, in principle, Nanodisc-membrane protein are assembled on native membrane-like structures and are completely detergent free. This opens up applications like immunization use for Nanodisc assembled proteins otherwise restricted due to detergent dissolving native cell membrane and causing damage to cells. In addition, the Nanodisc version of membrane proteins are compatible with cell-based assays and CAR expression detections. The Nanodisc platform used by ACRO has been authorized by the patent holder and can be used with confidence during the development process.
Claudin18.2-VLP is tested and verified by anti-Claudin18.2 specific antibodies. The purity is evaluated by SDS-PAGE/HPLC/DLS/SEM. The conventional negative dye EM cannot see whether Claudin18.2 is on the VLP due to its low resolution. Binding activity with anti-Claudin18.2 specific antibodies can confirm the presence of Claudin18.2 on the particles.
We currently store all VLP formulated products as liquids at -70°C and ship on dry ice. We do store non- enveloped VLP products by freeze-drying. VLP immunization mainly requires attention to the choice of adjuvant dose, because VLP itself can enhance immunogenicity, which is not the case for conventional protein products.
CD24 and PD-1 are soluble proteins. They are not multi-pass transmembrane proteins, so non-enveloped VLPs are used. While multi-transmembrane proteins have hydrophobic transmembrane regions and need to be embedded on the membrane of the enveloped VLPs. The difference between VLP and enveloped VLP is whether there is a phospholipid bilayer membrane on the surface of the VLP.
If customized, the membrane protein in VLP format is expected to take 6-8 weeks. The DDM/CHS version requires expression and purification conditions optimization of the target multi-pass transmembrane protein and detergent screening, so the development cycle is longer lasting more than 8 weeks. The customized Nanodisc version of membrane protein requires an additional 4 weeks on top of the DDM/CHS development time.
Authors: Lionel Rougé et al.
Journal: Science
Authors: Paige M. Glumac , Aaron M. LeBeau.
Journal: Glumac and LeBeau Clin Trans Med
Authors: Kenji Maeda, Debananda Das et al.
Journal: Journal of Biological Chemistry
Authors: Line Barington, Pia C. Rummel, et al.
Journal: Journal of Biological Chemistry
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.