Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>

































 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
> Insights > BA.2.75: After BA.5, the next generation of the most virulent strain may have appeared When BA.5 setting off a global wave of "reinfection" and was thought as the worst second-generation variant, a new variant, BA.2.75, appeared in India and seems to be taking BA.5 place. Although there are still a lot of unknown about the new variant, the critical mutations as well as the surprising transmission speed and the geographical extensiveness of BA.2.75 sequences have attracted the attention of experts and raised the potential danger signal.
To support the research about this new strain, ACROBiosystems has developed BA.2.75 related products at the first time. Now, the essential antigens including Spike trimer, S RBD and Nucleocapsid protein are all in stock! Antigens such as Spike NTD and antibodies, Pseudovirus, as well as ELISA kits for antigen or antibody detection are coming soon.
According to the data from GISAID, until 25th July, BA.5 was accounted for 52% of the sequence library, making it the dominant strain in a new global outbreak. Some research results showed that BA.5 seems to be the most infectious version of SARS-CoV-2 with the R0 value of 18.6 (about 2.79 in wild type). Furthermore, the strong immune escape ability is also a powerful blessing for BA.5 to quickly become the dominant strain. A report from New York showed that the breakthrough infection capacity of BA.5 should be 4.2 times of BA.1. The latest research shows that BA.5 has also a strong immune escape from the serum of BA.1 infected people, which means that the existing "immune wall" in the population may be ineffective against BA.5.
>> Related Article: Omicron recombinant strains and new variants are frequent, who is the stronger immune escape master?
While people lamented that BA.5 was the worst variant so far, a new variant, BA.2.75, has emerged in India and spread rapidly to more than a dozen of countries, including the United States, Britain, and Australia. Although it is not clear about its infectivity, hospitalization or the ability of immune escape, experts have raised potential red flags.
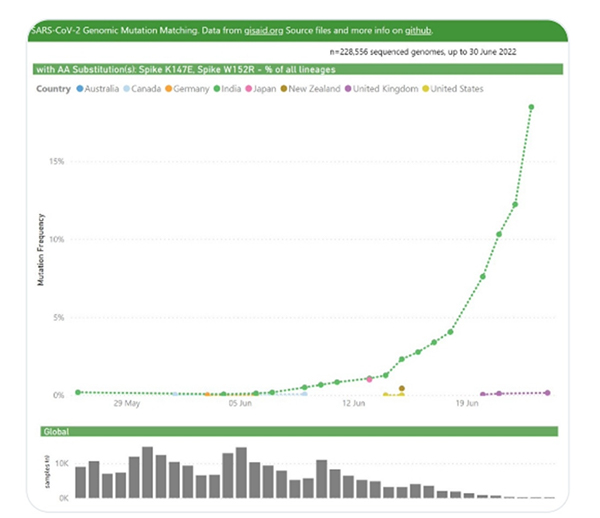
Dr. Eric Topol, the founder and director of the Scripps Research Institute in the US said that the BA2.75 variant has eight more mutations as compared to the emerging BA.5 strain, which may result in a stronger immune escape capacity. Tom Peacock, a virologist in the Department of Infectious Diseases at Imperial College London, tweeted that the Spike protein in BA.2.75 has many mutations. It is notable for its rapid growth and wide geographical distribution. According to another famous virologist Jesse Bloom from Fred Hutch, the sequence analysis of BA.2.75 shows that it contains 17 more nucleotide mutations than the previous generation of BA.2 mutations and contains two key mutations that have significant antigen-converting effects: G446S and Q493R on the Spike protein. Previous studies have shown that G446S is one of the most effective immune escape sites. The introduction of G446S mutation into BA.2 may result in decreased neutralization. On the other hand, Q493R may result from the increased affinity of the virus to the ACE2 receptor.
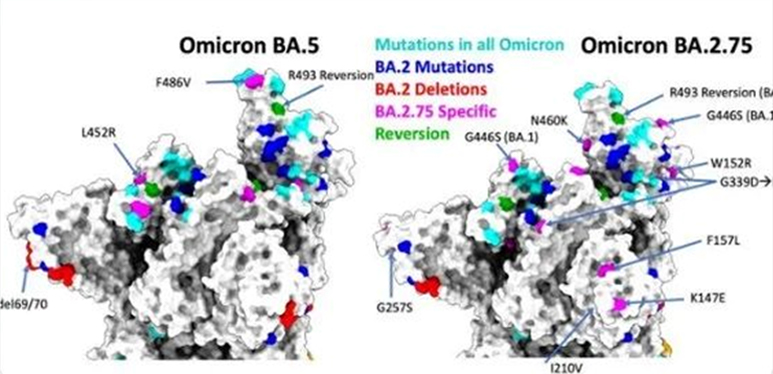
Although the number of tested samples and sequences is still small, as the first "second-generation variant" to be successfully transmitted to many countries, BA.2.75 still have attracted widespread attention because of the critical mutations and significant growth advantages. Therefore, the most important thing is to monitor and track this variant effectively and to study it as soon as possible. At the same time, more complex genetic changes may occur in the next evolution of the coronavirus.
ACROBiosystems has closely followed the development of COVID-19 pandemic and developed the BA.2.75 antigens and other core reagents at the first time, which are now available in stock. At the same time, to meet the needs of cross-research, products about BA.2.38, BA.2.74, and Ba.2.76 are also developed and can be preordered now.
| Lineage | Molecule | Cat.No. | Tag | Host | Mutation | Preorder/Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omicron | BA.2.75 | Spike RBD | SPD-C522t | His Tag | HEK293 | G339H, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, G446S, N460K, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H | |
| Omicron | BA.2.75 | Spike protein | SPN-C522f | His Tag | HEK293 | T19I, LPP24-26del, A27S, G142D, K147E, W152R, F157L, I210V, V213G, G257S, G339H, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, G446S, N460K, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, Q954H, N969K, R683A, R685A, F817P, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P | |
| Omicron | BA.2.75 | Spike NTD | SPD-C522x | His Tag | HEK293 | T19I, LPP24-26del, A27S, G142D, K147E, W152R, F157L, I210V, V213G, G257S | |
| Omicron | BA.2.76 | Spike RBD | SPD-C522v | His Tag | HEK293 | G339D, R346T, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H | |
| Omicron | BA.2.76 | Spike protein | SPN-C522i | His Tag | HEK293 | T19I, LPP24-26del, A27S, G142D, V213G, Y248N, G339D, R346T, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, Q954H, N969K, R683A, R685A, F817P, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P | |
| Omicron | BA.2.74 | Spike RBD | SPD-C522u | His Tag | HEK293 | G339D, R346T, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, L452M, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H | |
| Omicron | BA.2.74 | Spike protein | SPN-C522h | His Tag | HEK293 | T19I, LPP24-26del, A27S, G142D, V213G, G339D, R346T, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, L452M, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, Q954H, N969K, R683A, R685A, F817P, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P | |
| Omicron | BA.2.38 | Spike RBD | SPD-C522w | His Tag | HEK293 | G339D, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417T, N440K, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H | |
| Omicron | BA.2.38 | Spike protein | SPN-C522g | His Tag | HEK293 | T19I, LPP24-26del, A27S, G142D, V213G, G339D, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417T, N440K, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, Q954H, N969K, R683A, R685A, F817P, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P | |
| Omicron | BA.5 | Spike protein | SPN-C522e | His Tag | HEK293 | T19I, LPP24-26del, A27S, HV69-70del, G142D, V213G, G339D, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, L452R, S477N, T478K, E484A, F486V, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, Q954H, N969K, R683A, R685A, F817P, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P | |
| Omicron | BA.5 | Spike protein | SPN-C82Eu | His Tag & Avi Tag | HEK293 | T19I, LPP24-26del, A27S, HV69-70del, G142D, V213G, G339D, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, L452R, S477N, T478K, E484A, F486V, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, Q954H, N969K, R683A, R685A, F817P, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P | |
| Omicron | BA.5 | Nucleocapsid protein | NUN-C52Hx | His Tag | HEK293 | P13L, ERS31-33del, E136D, R203K, G204R, S413R |
>>> Click to see more other COVID-19-related products
>>> If you need other latest mutant-related products, please click here to leave a message
Assay data
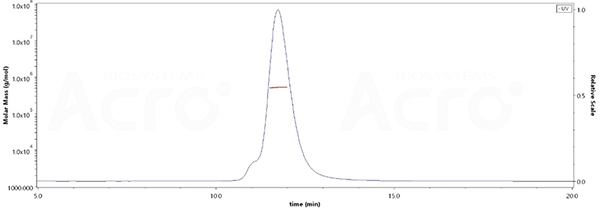
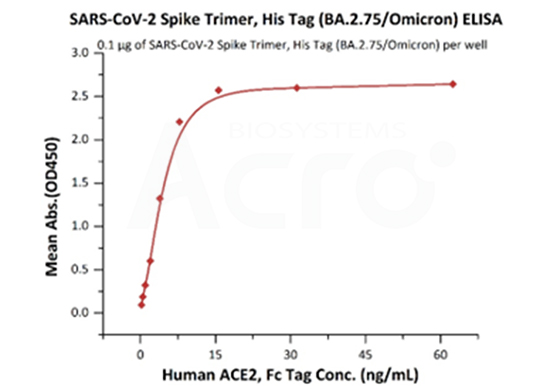
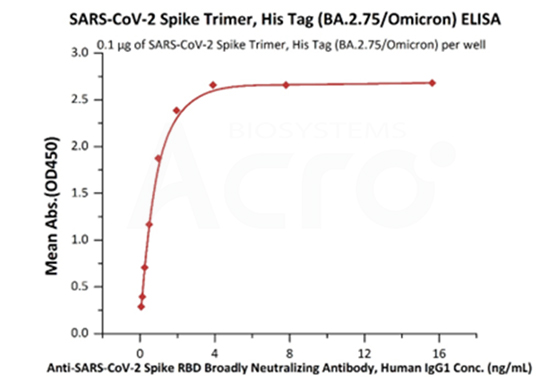
The purity of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Trimer, His Tag (BA.2.75/Omicron) (Cat. No. SPN-C522f) is more than 90% verified by SEC-MALS. The molecular weight of this protein is around 496-548 kDa.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.