 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
On 26 November 2021, WHO designated the variant B.1.1.529 a variant of concern, named Omicron. As of Nov 29th, confirmed cases of this new VOC Omicron have been reported in South Africa, Botswana and more than 12 other countries.
One reason of Omicron sparked global alarm owing to its unprecedented set of genetic mutations. Omicron is a highly divergent variant with 50 mutations and includes more than 30 on the spike protein. Furthermore, some familiar mutations identified on omicron also appeared on other VOCs, which gives rises concerns about its immune escape potential and higher transmissibility.
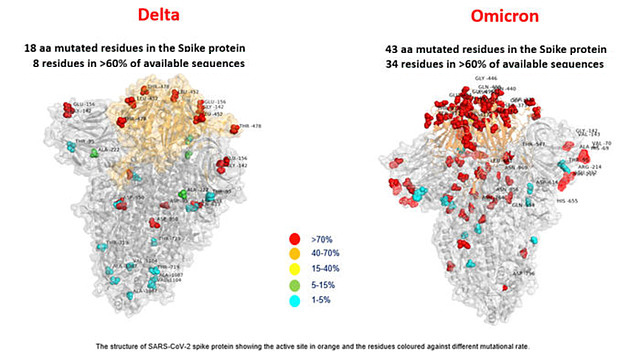
Mutation information are retrieved from Coronavirus Antiviral & Resistance Database1.
Another alarm is epidemiological and transmission speed of this variants. According to the result of PCR test, Omicron is responsible for more than 90 per cent of infections in Gauteng. The analysis of wastewater in Pretoria for traces of the Sars-Cov-2 virus — an indicator of outbreak size — suggested that infections had surged close to levels last seen during the Delta wave six months ago.
- G339D
G339D is a rare RBD core mutation that is present in the Omicron VOC. It has a slightly elevated escape fraction (0.048) for sotrovimab in the Bloom laboratory DMS assay.
- K417N
K417N/T are ACE2-binding site RBM mutations present in the Beta (K417N), Gamma (K417T), and Omicron (K417N) VOCs. K417N has also been reported in two sublineages of the Delta variant (AY.1 and AY.2). Both mutations reduce ACE2 binding. K417N confers >100-fold reduced susceptibility to etesivimab and ~30-fold reduced susceptibility to casirivimab but appears to retain susceptibility to the remaining mAbs in advanced clinical development. K417N/T retain full susceptibility to plasma samples from convalescent persons.
- N440K
N440K is an increasingly common RBD mutation, which is found in the Omicron VOC and in several other global lineages. It causes high-level resistance to imdevimab and C135, two mAbs that bind the RBD core region. It retains susceptibility to sotrovirmab, another core-binding mAb. Based on limited data, it does not appear to reduce susceptibility to most convalescent plasma samples.
- G446S
G446V is a rare RBD mutation in the ACE2 binding site. In one study it was reported to occur in 4.5% of REGN-COV2 (casirivimab+imdevimab) study participants at an allele fraction above 15%. It causes high-level resistance to imdevimab and C135. It retains susceptibility to casirivimab but has not been tested against most of the other mAbs in phase III trials. G446S is a rare mutation present in the Omicron VOC. It is associated with resistance to imdevimab in the Bloom laboratory DMS assay.
- S477N
S477N is a common RBM mutation that has increased gradually since the start of the pandemic and is present in the Omicron VOC. It increases the strength of ACE2 binding. It has not been shown to reduce susceptibility to any of the FDA EUA-approved mAbs.
- T478K
T478K is an RBD mutation present in the Delta VOC in combination with L452R and in the Omicron VOC in combination with multiple other RBD mutations. Its effects on mAbs and immune plasma have not been well-studied although it appears to retain unchanged binding to each of the EUA-approved mAbs. T478I is an uncommon RBD mutation, which has been shown to be susceptible to each of the EUA approved mAbs.
- E484A
E484 is recognized by a high proportion of the polyclonal Abs developing in SARS-CoV-2 infected persons. E484A is a rare mutation present in the Omicron VOC. It has been selected in vitro by several mAbs and in vivo by bamlanivimab and casirivimab/imdevimab. It greatly reduces susceptibility to C121, C144, and several additional mAbs.
- Q493K
Q493R/K are rare ACE2-binding site RBD mutations selected in vitro by casirivimab, bamlanivimab and several other mAbs. They associated with reduced binding to bamlanivimab, etesivimab, and casirivimab and reduced neutralization by multiple vaccine-elicited mAbs. They have also been reported in patients with prolonged infections. Q493R is present in the Omicron VOC.
- Q498R
Q498H is a rare RBD mutation which appears to increase binding to both the human and mouse ACE2 receptor. Q498R is present in the Omicron VOC.
- N501Y
N501Y is an ACE2-binding site RBM mutation present in the Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Omicron VOCs. N501Y increases ACE2-binding and increases virus replication in human upper airway cells. N501Y does not influence the binding and neutralization of most mAbs. N501Y alone is rarely associated with reduced susceptibility to convalescent plasma or plasma from persons receiving the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2, Moderna mRNA-1273, or Novavax NVX-CoV2373 vaccines.
- Δ69-70
NTD deletions at positions 69/70 are present in the Alpha and Omicron VOCs and in the Eta VOI. They are associated with increased virus replication. They do not reduce susceptibility to neutralizing mAbs or convalescent plasma. This deletion prevents the amplification of one of three genomic segments in a commonly used diagnostic PCR assay, resulting in a phenomenon referred to as S-gene target failure (SGTF). SGTF has been used as a proxy for the Alpha variant in regions in which this variant co-circulated with other variants lacking this deletion.
- P681H
P681H is proximal to the S1/S2 furin cleavage site. It is present in the Alpha and Omicron VOCs and Theta VOI and in an increasing number of global lineages.P681R is also present in the Delta VOC and Kappa VOI and in A.23.1. The increased positive charge associated with both mutations appears to influence virus tropism by increasing S1/S2 cleavage in human airway epithelial cells.
- Δ143-145
NTD deletions between positions 141-146 occur in the Alpha and Omicron VOCs and in the Eta VOI. They are associated with resistance to several NTD-binding neutralizing mAbs but do not appear to reduce the neutralizing activity of plasma from convalescent or vaccinated persons.
- H655Y
H655Y occurs in the Gamma and Omicron VOCs and many other SARS-CoV-2 lineages. It increases spike protein cleavage and replication in vitro.
- N679K
Mutations just upstream of the S1/S2 furin cleavage including Q675H/R, Q677H/P, N679K, and P681H/R have occurred independently in many SARS-CoV-2 global lineages.
- G142D & T95I
G142D and T95I are common NTD mutations present in the Delta and Omicron VOCs.
In addition, some rare RBD core mutations, including S371L, S373P, S375F, G496S, Y505H, T547K, D796Y, were identified in the Omicron VOC and need further studies.
ACROBiosystems are going full steam ahead on the development of Omicron recombinant antigens and other related products. The first batch of the products will still be limited and on first come first served basis. We highly recommend you to send us official PO to secure the products .
| Molecule | Cat.No. | Tag | Mutation | Product description | Preorder/Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spike RBD | SPD-C522e | His Tag | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493K, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H | SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) | |
| Spike RBD | SPD-C82E4 | His Tag & Avi Tag | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493K, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H | Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, His,Avitag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) | |
| Spike protein | SPN-C52Hz | His Tag | A67V, HV69-70del, T95I, G142D, VYY143-145del, N211del, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493K, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F | SARS-CoV-2 Spike Trimer, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) | |
| Spike protein | SPN-C82Ee | His Tag & Avi Tag | A67V, HV69-70del, T95I, G142D, VYY143-145del, N211del, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493K, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F | Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike Trimer, His,Avitag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) | |
| Spike NTD | SPD-C522d | His Tag | A67V, HV69-70del, T95I, G142D, VYY143-145del, N211del, L212I, ins214EPE | SARS-CoV-2 Spike NTD, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) | |
| Spike S1 | S1N-C52Ha | His Tag | A67V, HV69-70del, T95I, G142D, VYY143-145del, N211del, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493K, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H | SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) | |
| Nucleocapsid protein | NUN-C52Ht | His Tag | P13L, ERS31-33del, R203K, G204R | SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) |
https://covdb.stanford.edu/sierra/sars2/by-patterns/report/
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
