 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
> Insights > How to crack the insufficient response of PD-1 inhibitors? Combination therapy to break the game! On October 18, 2021, Innovent Announces TYVYT® (Sintilimab Injection) in combination with Avastin ® (Bevacizumab injection) and chemotherapy in patients with EGFR-Mutated nonsquamous non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Prior EGFR-TKI Treatment, has Met Primary Endpoint.
This is the world's first prospective, double-blind, multi-center trial and Phase 3 Study which confirmed that PD-1 inhibitors combined with anti-vascular drugs and chemotherapy significantly improved PFS in EGFR-mutated non-squamous NSCLC populations with EGFR-TKI treatment progress.
PD-1 inhibitors are exploding in popularity.
Immunotherapy has achieved excellent therapeutic results in a variety of tumors therapy such as melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Among them, antibodies against programmed death-1 (PD-1) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) are the latest breakthroughs in cancer immunotherapy. To date, PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors represent the most successful class of drugs in the history of new drugs. Early preclinical evidence shows that the activation of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibits the activation and proliferation of tumor antigen-specific T cells and promotes tumorigenesis, which negatively regulates the immune function of T cells. Blocking this interaction activates the immune system to fight cancer.
Various pharmaceutical companies have conducted about 500 clinical studies on different types of antibodies, involving as many as 20 entities and hematological malignancies. At present, the FDA has approved five antibodies for PD-1 PD-1 /PD-L1 signal blocking to treat various types of cancer. In addition, there are some antibodies in clinical trials which will used to block PD-1 /PD-L1 pathway.
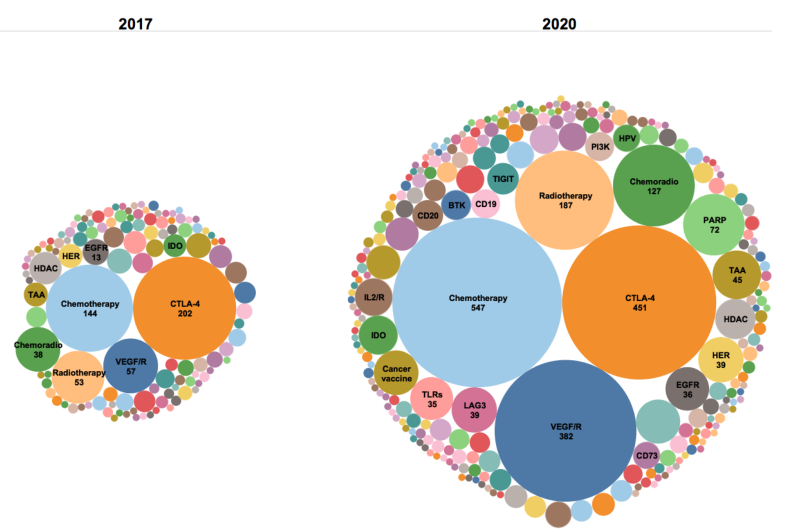
A combination of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: the prospect of overcoming the weakness of tumor immunotherapy
Although PD-1 inhibitors have achieved matchless success among similar drugs, not all patients have responded to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor treatment when used as a monotherapy, the high cost of treatment, or resistance because complex immune regulatory signaling pathway has occurred after treatment. In view of the clinical limitations of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy, there is a requirement to explore novel alternative strategies and personalized immunotherapy strategies through a combination of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with small molecular targets, chemotherapy and radiotherapy to improve sensitivity to activated anti-tumor immune response and the response rate of patients and solve the bottleneck of drug resistance .
Chemotherapy usually kills cancer cells by targeting their DNA synthesis and replication. It also promotes the presentation of tumor antigens following cancer cell death, activates tumor specific T cells, facilitates DCs maturation, stimulates type I interferon response and eliminates bone marrow-derived immunosuppressive cells. Therefore, an appropriate combination of chemotherapy drugs and PD-1 inhibitors can enhance the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors, especially in chemotherapy-sensitive tumors with low immunogenicity. Immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with chemotherapy have been successfully used in non-small cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-189,IMpower130), Small cell lung cancer(KEYNOTE-407,IMpower133)and triple negative breast cancer(KEYNOTE-355,IMpassion13.
Radiotherapy is believed to change the differentiation and function of T cells and promote the expression of PD-L1, which means that increasing radiotherapy can enhance the effect of anti-PD-L1 treatment. In clinical trials and preclinical models, radiotherapy has shown synergy with various immunotherapies. According to preclinical studies, the combination of PD-1 inhibitors and radiotherapy can activate CTL and reduce myelogenous inhibitory cells.
It can be used in combination with other immune checkpoint inhibitors. For example, the classic combination therapy that blocks PD-1+CTLA-4 improves the efficacy. The combination of CTLA-4 (ipilimumab) and PD-1 (nivolumab) antibodies can bring survival benefits to patients with melanoma or renal cell carcinoma. However, the incidence of adverse reactions is higher than that of monotherapy alone. Clinical trials of PD-1 inhibitors in combination with other inhibitory-receptors such as Lag-3 and Tim3 are underway.
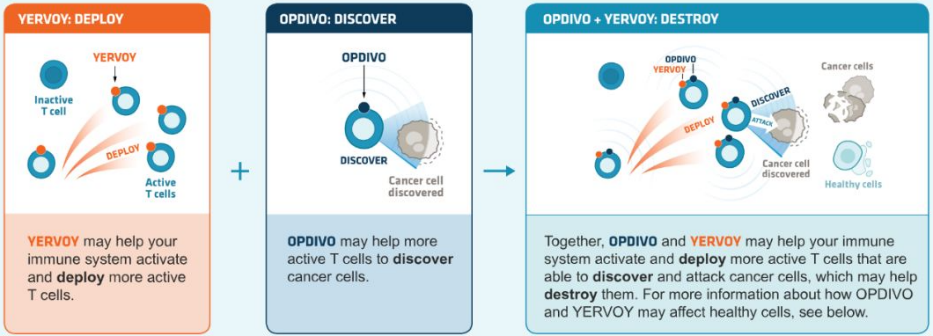
Source: BMS official Website, Zhongkang Industrial Capital Research Center
Agonist can enhance the antitumor immune response enabled by PD-1 blocking. Agonist antibodies against co-stimulating molecules such as CD137 (4-1BB), CD134 (OX40), CD357 (glucocorticoid-induced TNFR; GITR) and CD40 have provided lasting response tests in preclinical studies and clinical studies of mouse tumor models. Some research results show that the combined application of 4-1BB agonist and PD-1 blocker has produced synergistic effects in preclinical studies. Phase I/Ib clinical trials of GWN323, a combined anti-GITR monoclonal antibody, and PDR001, an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, are in progress. Clinical trials of the OX40 agonist MEDI6469 in combination with the anti-PD-L1 antibody MEDI4736 are also under development.
Immune checkpoint blockade and chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T) cell therapy are antibody-based therapies and cell-based therapies, respectively, and play an important role in the fight against cancer. The combination of CAR-T cell therapy and PD-1 blockers has been used to enhance the therapeutic effect of preclinical models and clinical trials. For example, in one study, a patient with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma recovered to CD19 CAR-T cells after pembrolizumab treatment.
T-cell recruitment bispecific antibody (TCB) occupies 50% of the bispecific antibody pipeline, but if the T-cell itself is exhausted, it cannot have the activity of killing tumors. Therefore, combining PD-1 antibodies to restore T-cell activity can theoretically enhance anti-tumor activity. TCB can increase the redirect of T cells to tumors and overcome the problem that tumors are not sensitive to PD-1 antibodies.
Other treatments combined with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors include vaccines, cytokine therapy, and chemokine inhibition. Cancer vaccines present antigens to the immune system to produce antitumor immune responses. Since the role of PD-1 blockers is to initiate a natural immune response, combining cancer vaccines with PD-1 blockers may be a reasonable way to treat tumors with low immunogenicity.
For the combination with cytokines, most of research are focusing on the combination of PD-(L)1 and VEGF(R). Mechanically speaking, bevacizumab targeting VEGF itself has an anti-angiogenic effect, which not only has a direct impact on tumor angiogenesis and cancer cell proliferation, but also enhances tumor immunogenicity and T cell infiltration. The combination of bevacizumab and anti-PD-(L)1 monoclonal antibody can enhance the response of activated T cells to tumor antigens and further enhance the ability to kill cancer cells.
To support the above research, ACROBiosystems developed a series of high-quality immune checkpoint proteins base on its own technology platform, including PD-1 and PD-L1, which can be widely used in immunition, antibody screening, cell based assay,PK, etc.
The products have the following characteristics:
 The company's products are rich and diverse, covering multiple species and labels.
The company's products are rich and diverse, covering multiple species and labels.
 Verified by MALS for high purity, purity greater than 90%;
Verified by MALS for high purity, purity greater than 90%;
 ELISA/SPR/FACS verification of high bioactivity
ELISA/SPR/FACS verification of high bioactivity
 The antibody binding activity has been verified by the marketed antibody drug (Nivolumab).
The antibody binding activity has been verified by the marketed antibody drug (Nivolumab).
In addition, ACROBiosystems has provided a series of CAR-T and bispecific antibody target proteins.
Product list
| Cat. No. | Speices | Product Description | Preorder/Order |
|---|---|---|---|
| PD1-H82E4 | Biotinylated Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Avitag™,His Tag (recommended for biopanning) (MALS verified) | Human | |
| PD1-H5221 | Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His Tag (MALS Verified) | Human | |
| PD1-H5257 | Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc Tag, low endotoxin (MALS Verified) | Human | |
| Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Strep Tag | Human | ||
| PD1-H82F1 | Biotinylated Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc,Avitag™ (MALS verified) | Human | |
| PD1-H5259 | Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Llama IgG2b Fc Tag, low endotoxin | Human | |
| PD1-H522a | Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His Tag, low endotoxin (MALS verified) | Human | |
| PD1-H5255 | Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Mouse IgG2a Fc Tag (HPLC-verified) | Human | |
| PD1-HP2F2 | PE-Labeled Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc,His Tag (recommended for neutralizing assay) | Human | |
| PD1-H82F4 | Biotinylated Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc,Avitag™,His Tag (MALS verified) | Human | |
| PD1-H52H6 | Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Full Length Protein, His Tag | Human | |
| PD1-H82A4 | Biotinylated Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Mouse IgG2a Fc,Avitag™ (MALS verified) | Human | |
| PD1-H52H2 | Human PD-1 Protein, His tag (Nanoparticle) | Human | |
| PD1-M82F4 | Biotinylated Mouse PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc,Avitag™ (MALS Verified) | Mouse | |
| PD1-M5228 | Mouse PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His Tag | Mouse | |
| PD1-M5259 | Mouse PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc Tag | Mouse | |
| PD1-R52H2 | Rat PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His Tag | Rat | |
| PD1-R5253 | Rat PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc Tag | Rat | |
| PD1-C5254 | Cynomolgus PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc Tag | Cynomolgus | |
| PD1-C82E6 | Biotinylated Cynomolgus PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His,Avitag™ | Cynomolgus | |
| PD1-R52H3 | Rhesus macaque PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) | Rhesus macaque | |
| PD1-R52H0 | Rabbit PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) | Rabbit | |
| PD1-RB5251 | Rabbit PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc Tag | Rabbit | |
| PD1-C52H9 | Canine PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) | Canine |
Assay data
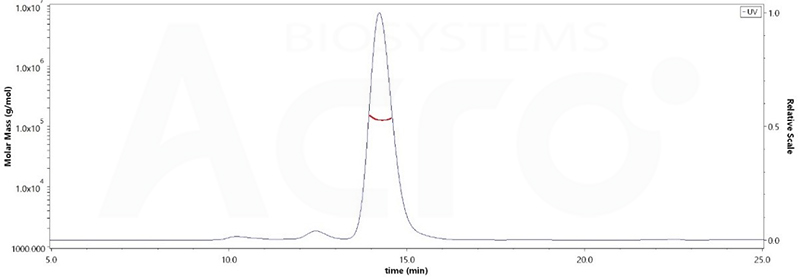
The purity of Human PD-1, Fc Tag, low endotoxin (Cat. No. PD1-H5257) was more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 105-145 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
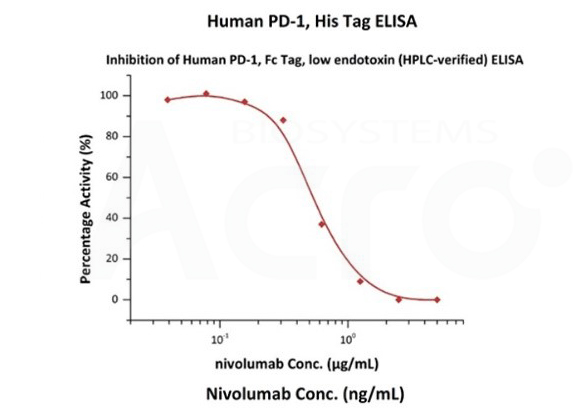
Nivolumab with a linear range of 0.1-3 ng/mL. Serial dilutions of nivolumab were added into Human PD-1, Fc Tag, low endotoxin (Cat. No. PD1-H5257): Biotinylated Human PD-L1, Fc, Avitag, His Tag (Cat. No. PD1-H82F3) binding reactions. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is 0.5381 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
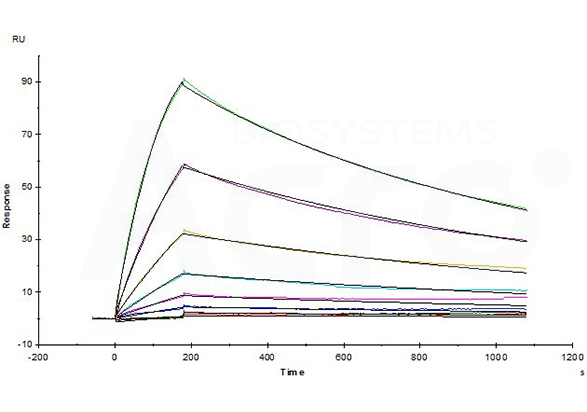
Opdivo (Nivolumab) captured on CM5 chip via anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface, can bind Human PD-1, His Tag (Cat. No. PD1-H5221) with an affinity constant of 4.94 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore T200) (Routinely tested).
[1] Chowdhury P S , Chamoto K , Honjo T . Combination therapy strategies for improving PD-1 blockade efficacy: A new era in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Journal of Internal Medicine, 2017.
[2] Xu J , Wang Y , Shi J , et al. Combination therapy: A feasibility strategy for CAR-T cell therapy in the treatment of solid tumors:[J]. Oncology Letters, 2018, 16(2):2063-2070.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
