Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>

































 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
> Insights > Interpreting the Association Between Cytokines and Autoimmune Diseases--Topic 2 Globally, autoimmune diseases are the second largest disease market after cancer. In 2022, the global autoimmune disease drug market was $132.3 billion, and this is projected to grow to $176.7 billion by 2030. Therefore, the autoimmune field is a highly competitive territory that major pharmaceutical companies are pursuing.
Building upon our previous exploration of cytokines involvement in rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis in Topic1, this article delves into the connection between cytokines and other prevalent autoimmune diseases.
Psoriasis
Type 1 Diabetes
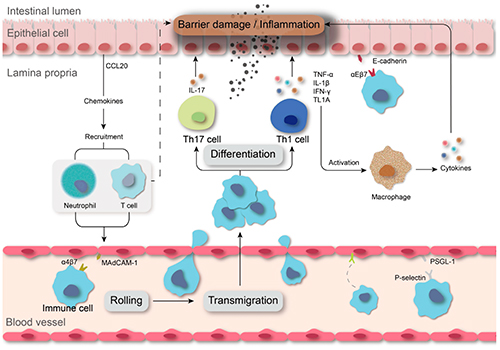
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
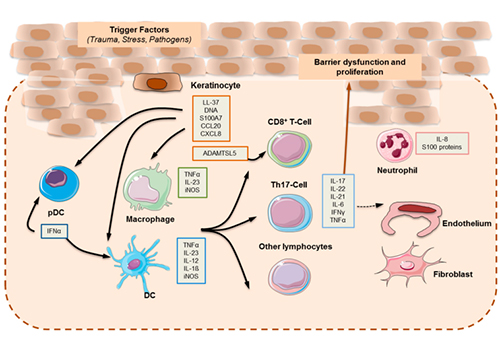
Psoriasis (PS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease associated with abnormal expression of various cytokines and immune system dysfunction. In-depth understanding and intervention of the abnormal expression of cytokines can support the understanding of disease progression and develop more effective treatments.
The overproduction of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) lead to abnormal proliferation of skin cells and exacerbation of the inflammatory response, thereby forming PS lesions. The abnormal expression of interleukin-23 (IL-23) promote the activation of immune cells and the enhancement of the inflammatory response, leading to the formation of PS lesions. Furthermore, interleukin-17 (IL-17) participates in the development of PS lesions by promoting the production of inflammatory mediators and the exacerbation of the inflammatory response.
Therapeutic drugs, such as the anti-TNF-α drug Etanercept, the anti-IL-23 drug Risankizumab, and the anti-IL-17 drug Bimekizumab, have been widely used in the treatment of PS. These drugs can modulate the immune response, reduce inflammation, and inhibit the abnormal proliferation of skin cells, thereby improving the symptoms and lesions of PS.
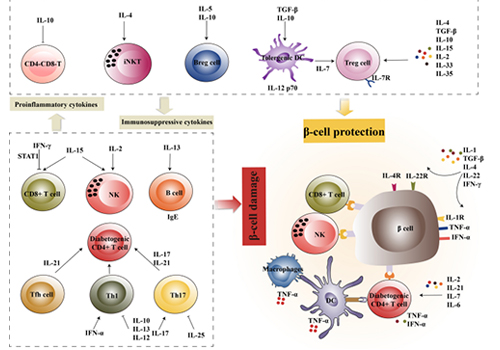
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is a chronic autoimmune disease, while in the development of T1D, cytokines play a crucial role in coordinating the complex multicellular interactions between pancreatic β cells and immune cells, making them potential targets for immunotherapeutic interventions.
Cytokines such as IL-10, TGF-β, IL-5, IL-4, IL-2, IL-15, IL-33 and IL-35 could induce regulatory phenotypes in immune cells, thereby releasing anti-inflammatory cytokines and exerting anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-α, IL-17 and IL-21 amplify inflammation through the proliferation and activation of immune cells in T1D. Due to the pleiotropic nature of cytokines, a given cytokine, such as IL-15, may trigger the activation of both diabetogenic and regulatory immune cells. Furthermore, B cells express high levels of cytokine receptors, such as IL-1R, IL-4R and IL-22R, and exhibit increased sensitivity to cytokines. Studies have shown that low-dose IL-2 favors the development of the Treg population, thereby controlling the onset and progression of T1D.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) includes Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. The pathogenesis of these diseases involves abnormal expression of various cytokines and dysregulation of the immune system.
In IBD, TNF-α and various interleukin family proteins participate in the intestinal inflammatory response, mucosal damage, and immune dysregulation. IL-1 is involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses, and its over-production in IBD may lead to intestinal damage and aggravation of inflammation. IL-6 participates in the regulation of inflammation and immune responses, and its high expression is associated with disease activity and severity. IL-12 and IL-23 are pro-inflammatory cytokines that participate in the inflammatory response and intestinal mucosal damage. Elevated expression of IL-17 is also positively correlated with IBD. Therefore, modulating these cytokines has become an important strategy for the treatment of IBD.
ACROBiosystems is providing you with a series of recombinant cytokines and their receptors, including Interleukins, Growth Factors, TNFs, Chemokines, CSFs, IFNs, and Complement Components with high purity, high bioactivity, and high batch-to-batch consistency to accelerate your autoimmune diseases drug development programs.
We have launched ClinMax™ ready-to-use ELISA kits with rigorously quality control, ensuring the precision, stability, and consistency of the analysis results, to better meet your experimental needs.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.